Types of Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB’s)
Types of Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB’s)
MCBs are classified into three major types according to their instantaneous tripping currents. They are
- Type B MCB
- Type C MCB
- Type D MCB
Type B MCB
This type of MCB will trip instantly at a rate of three to five times its rated current. These are normally used for resistive or small inductive loads where switching surges are very small. Therefore, these are suitable for residential or light commercial installations.
Type C MCB
This type of MCB will trip instantly at a rate of five to ten times its rated current. These are normally used for high inductive loads where switching surges are high such as small motors and florescent lighting. In such cases, type C MCBs are preferred to handle higher value of short circuit currents. Therefore, these are suitable for highly inductive commercial and industrial installations.
Type D MCB
This type of MCB will trip instantly at a rate of ten to twenty five times its rated current. These are normally used for very high inductive loads where high inrush current are very frequent. These are suitable for specific industrial and commercial applications. The common examples of such applications include x-ray machines, UPS systems, industrial welding equipment, large winding motors, etc.
The above three types of MCBs provide protection within one tenth of a sec. The minimum and maximum trip currents of these MCBs are given in a tablular form below, where Ir is the rated current of the MCB. MCBs can also be classified based on number of poles such as single pole, double pole, triple pole and four pole MCBs.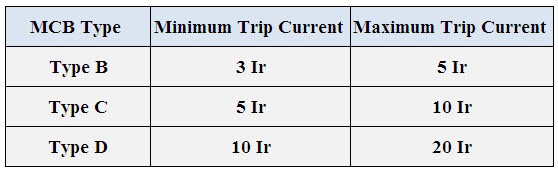

How to Select Proper MCB for different loads?
Choosing a particular MCB for a specific application is a careful task to ensure reliable protection against overloads and short circuits. If it is not selected according to the circuit requirements, there will be chances to lead frequent unwanted trippings. before we going in details, We must know difference between MCB & MCCB, How to Read MCB Nameplate and difference between ELCB, RCB and RCD Circuit Breakers
If it is undersized (MCB rating less than the nominal load current), MCB causes frequent tripping and causes to interrupt the current to the load it is being connected, because the MCB nominal current less than nominal current value of the load. Similarly, if it is oversized (MCB rating more than the nominal load current), the load to it is connected will not be protected efficiently. In such case, the MCB will not trip even though load is drawing overcurrents.
The following are the three factors to be considered for selecting an MCB for specific application.
1. Nominal rating of the circuit breaker
This is the rated ampere current rating of MCB. This value must be lower than the current carrying capacity of wiring system and higher than or equal to the maximum full load current in the wiring system. Generally, this rating should be such that it can handle 125 percent of continuous load plus rating of noncontinuous load. Typically this can be expressed as
Maximum full load current in the system ≤ Current rating of MCB ≤ Cable rating
2. KA rating or breaking capacity
This rating refers to the capability of MCB that can trip or interrupt the circuit under short circuit conditions. It is expressed in Kilo Amps (KA). This rating must not be less than the prospective short-circuit current. The prospective short-circuit current the maximum current that exist in the circuit during short-circuit conditions. In residential installations 6KA MCB is sufficient while 10 KA or above rating MCB is needed for commercial and light industrial applications.
3. Type of MCB
The type of MCB needed for a specific application decided by operating characteristics such that various current ratings are required to operate the loads instantaneously. We have already mentioned various types of MCBs for different applications above.
Application and Used of MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
As the main functions and applications has been already described in the above statements, the very basic uses of MCB is that it is used to protect a circuit (wiring, connected load and equipments etc) in case of:
- Short Circuit
- Over Current
- Over Load
You may also read:
Types of Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB’s)
 Reviewed by Article
on
September 08, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Article
on
September 08, 2018
Rating:
 Reviewed by Article
on
September 08, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Article
on
September 08, 2018
Rating:






